[drawattention]
Research and Innovation
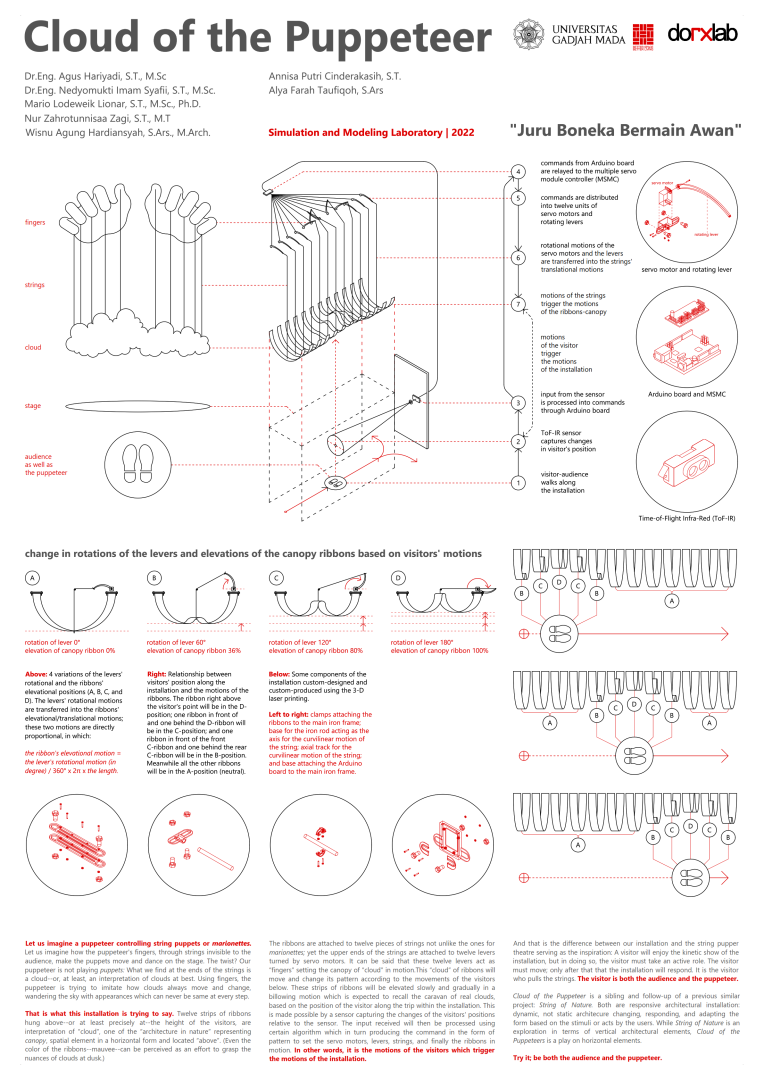
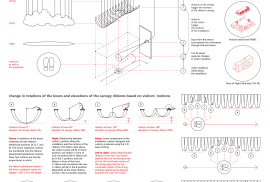
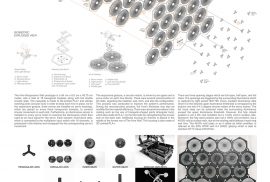
Let us imagine a puppeteer controlling string puppets or marionettes. Let us imagine how the puppeteer’s fingers, through strings invisible to the audience, make the puppets move and dance on the stage. The twist? Our puppeteer is not playing puppets: What we find at the ends of the strings is a cloud–or, at least, an interpretation of clouds at best. Using fingers, the puppeteer is trying to imitate how clouds always move and change, wandering the sky with appearances which can never be same at every step.
Journal title : Investigation into the daylight performance of expanded-metal shading through parametric design and multi-objective optimisation in Japan
Pada hibah penelitian dosen muda UGM tahun 2021, telah dilakukan penelitian mengenai hubungan sistem eksoskeleton pada bangunan tinggi terhadap visual interest di dalam ruangan. Adapun rangkuman dari hasil simulasi dan penelitian tersebut adalah sebagai berikut :
Journal title : Effectiveness of adaptive façade with helicon mechanisms on energy values and natural lighting in Indonesia
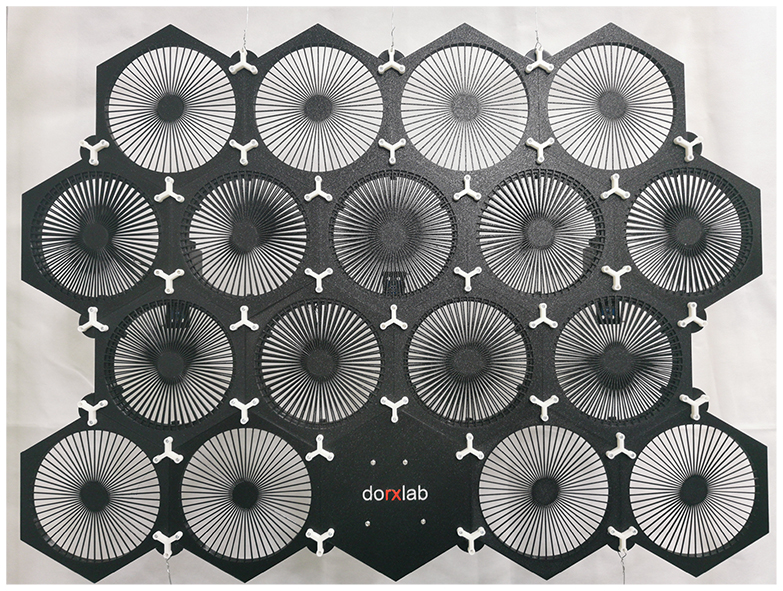

Model prototipe Hive Responsive Wall berukuran 64 cm x 6,5 cm x 48,75 cm, dengan total 18 modul heksagonal (red: Hive) bersama dengan bilah-bilah melingkar ganda. Maket model dibuat dengan memanfaatkan 3D printer dan menggunakan bahan PLA+. Setial Hive menggunakan sambungan takik (kunci melingkar) untuk menjaga setiap modul tetap di tempatnya. Sedangkan untuk gerakan responsif, tiga servo dipasang pada box servo, yang ditempatkan pada setiap tiga modul Hive, untuk melakukan gerakan melingkar pada setiap slat. Selanjutnya, sensor iluminansi dipasang pada setiap motor servo untuk memeriksa iluminasi. Sensor ini juga yang kemudian memberikan sinyal input untuk servo. Data illuminasi yang ditangkap oleh sensor dikirimkan ke multiplexer yang memiliki 16 channels. Arduino akan memproses data ini, kemudian mengirimkan sinyal kepada servo untuk menggerakkannya sesuai pemetaan dan pemrograman yang telah disiapkan sebelumnya.
Journal title : A Modular Interlocking Element for Material-Efficient Stereotomy Construction

Seperti pada kerai kinetik otomatis lainnya, tindakan meningkatkan kinerja bangunan dengan mempersempit fenestrasi berdampak pada penurunan kenyamanan visual dalam ruangan. Secara hipotetis, visibilitas dalam ruangan dapat ditingkatkan dengan terus-menerus menggerakkan tirai, sambil tetap mempertahankan konsumsi energi bangunan. Jenis pengembangan Sudare ini disebut Buzzing Sudare.
Journal title: The Comparison of Device Material of Sliding Sudare Using a Prototyping Method
Conference paper title: Parametric Roster Concrete Brick Modules as External Shading Device to Maximize Indoor Visual Comfort